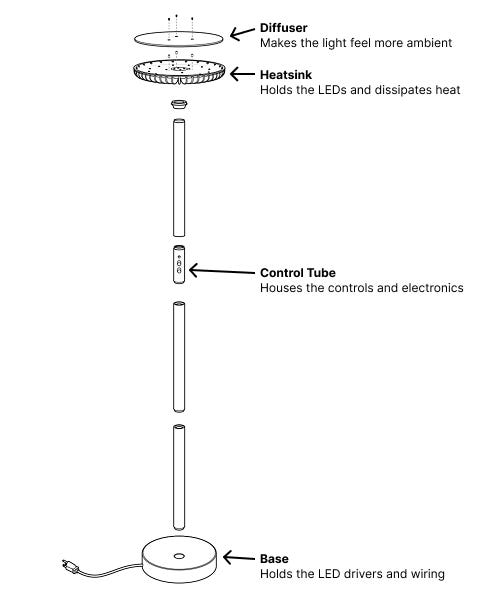
Lessons Learned Shipping 500 Units of my First Hardware Product
Building in consumer hardware as a software engineer
1 year ago (Jan 2025) I quit my job as a software engineer to launch my first hardware product, Brighter, the world’s brightest lamp. In March, after $400k in sales through our crowdfunding campaign, I had to figure out how to manufacture 500 units for our first batch. I had no prior experience in hardware; I was counting on being able to pick it up quickly with the help of a couple of mechanical/electrical/firmware engineers.
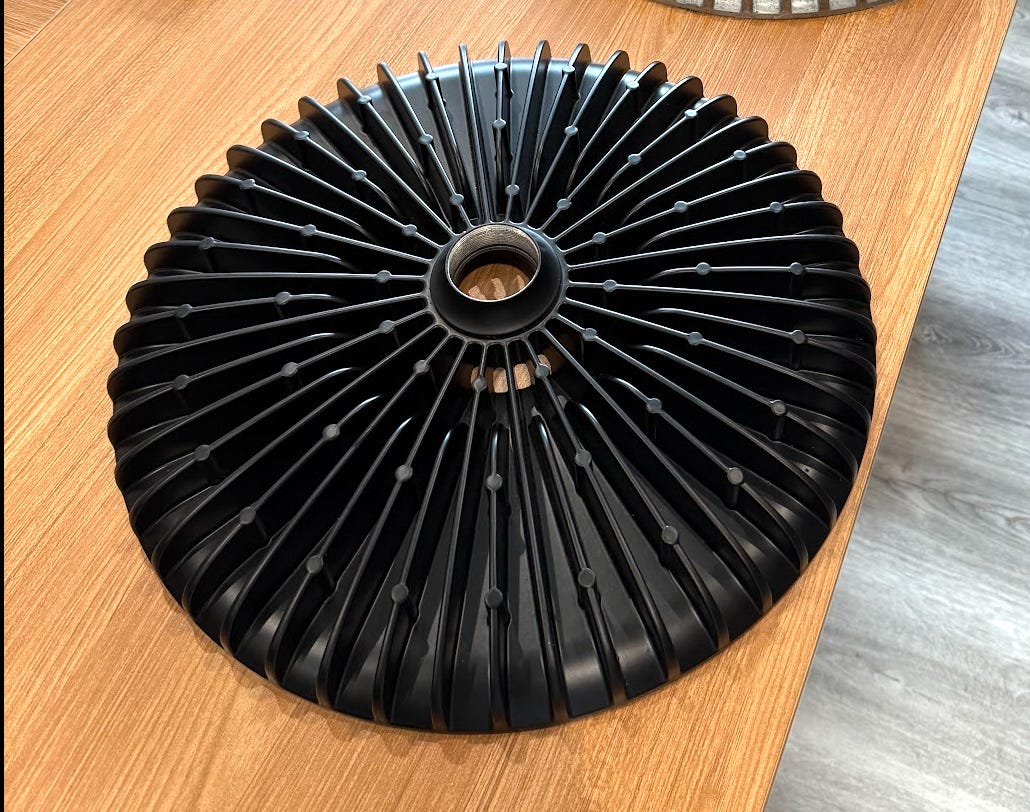
The problems began immediately. I sent our prototype to a testing lab to verify the brightness and various colorimetry metrics. The tagline of Brighter was it’s 50,000 lumens — 25x brighter than a normal lamp. Instead, despite our planning & calculations, it tested at 39,000 lumens causing me to panic (just a little).
So with all hands on deck, in a couple of weeks we increased the power by 20%, redesigned the electronics to handle more LEDs, increased the size of the heatsink to dissipate the extra power, and improved the transmission of light through the diffuser.
This time, we overshot to 60,000 lumens but I’m not complaining.
Confident in our new design I gave the go ahead to our main contract manufacturer in China to start production of mechanical parts. The heatsink had the longest lead time as it required a massive two ton die casting mold machined over the course of weeks. I planned my first trip to China for when the process would finish.
Simultaneously in April, Trump announced “Liberation Day” tariffs, taking the tariff rate for the lamp to 50%, promptly climbing to 100% then 150% with the ensuing trade war. That was the worst period of my life; I would go to bed literally shaking with stress. In my opinion, Not Cool!
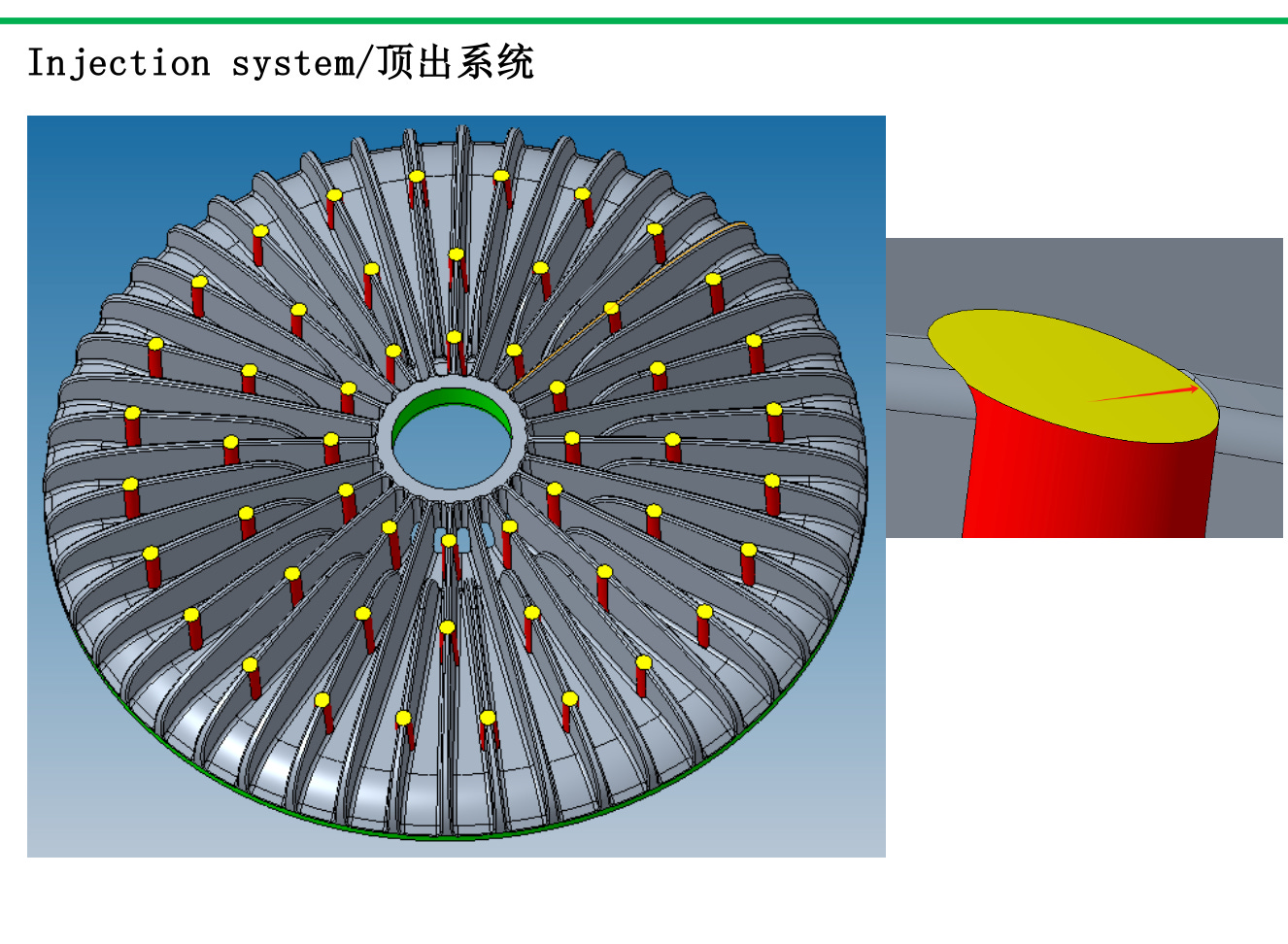
I was advised to press forward with manufacturing because 150% is bonkers and will have to go down. So 2 months later in Zhongshan, China, I’m staring at a heatsink that looks completely fucked. Due to a miscommunication with the factory, the injection pins were moved inside the heatsink fins, causing the cylindrical extrusions below. I was just glad at least the factory existed.
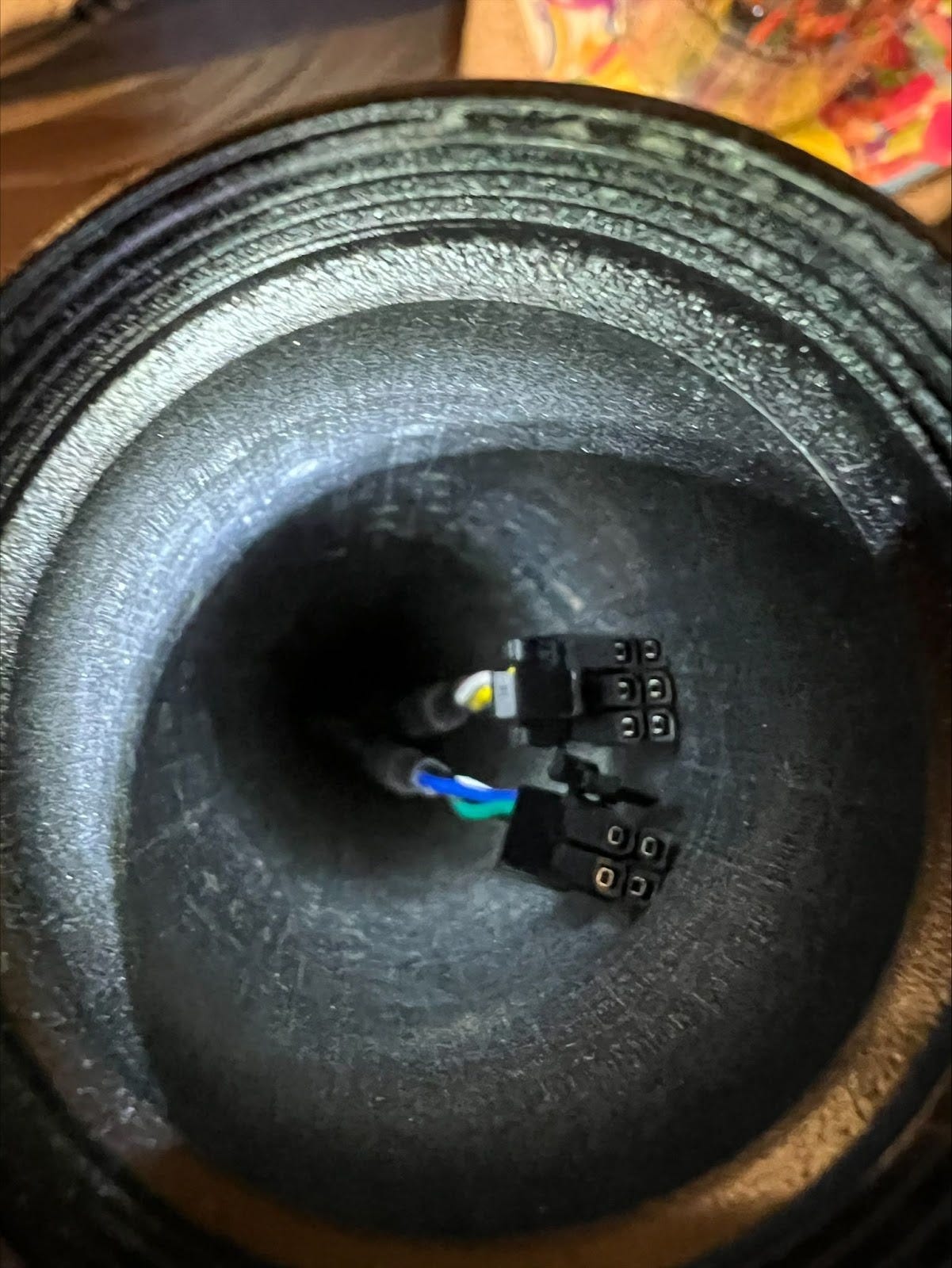
I returned in August to test the full assembly with the now correct heatsink. At my electronics factory as soon as we connect all the wiring, we notice the controls are completely unresponsive. By Murphy’s Law (anything that can go wrong will go wrong), I had expected something like this to happen, so I made sure to visit the factory at 10am China Standard time, allowing me to coordinate with my electrical engineer at 9pm ET and my firmware engineer at 7:30am IST. We’re measuring voltages across every part of the lamp and none of it makes sense. I postpone my next supplier visit a couple days so I can get this sorted out. At the end of the day, we finally notice the labels on two PCB pins were swapped.
With a functional fully assembled lamp, we OK mass production of the electronics.
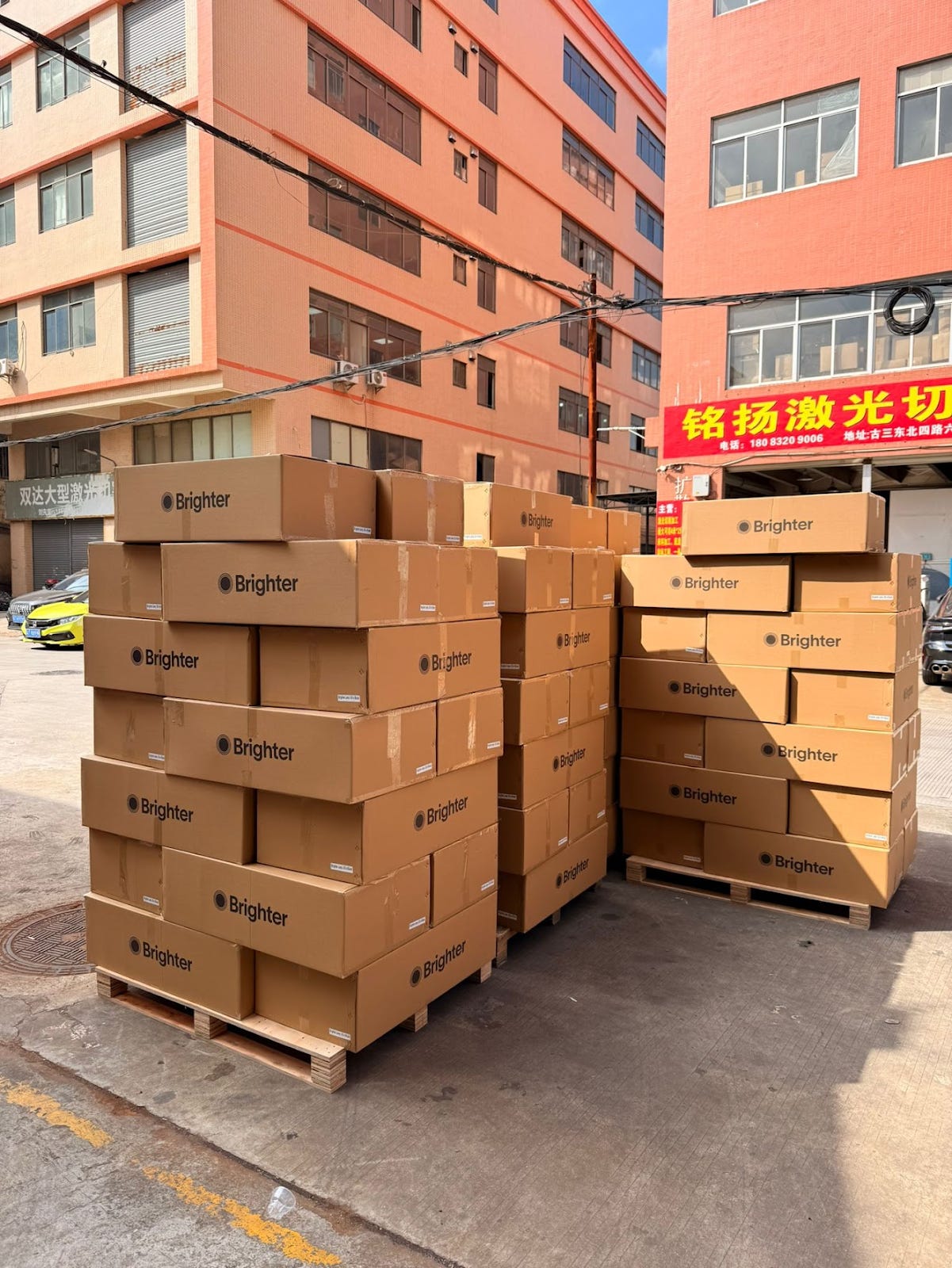
Our first full pieces from the production line come out mid October. I airship them to San Francisco, and hand deliver to our first customers. The rest are scheduled for container loading end of October.
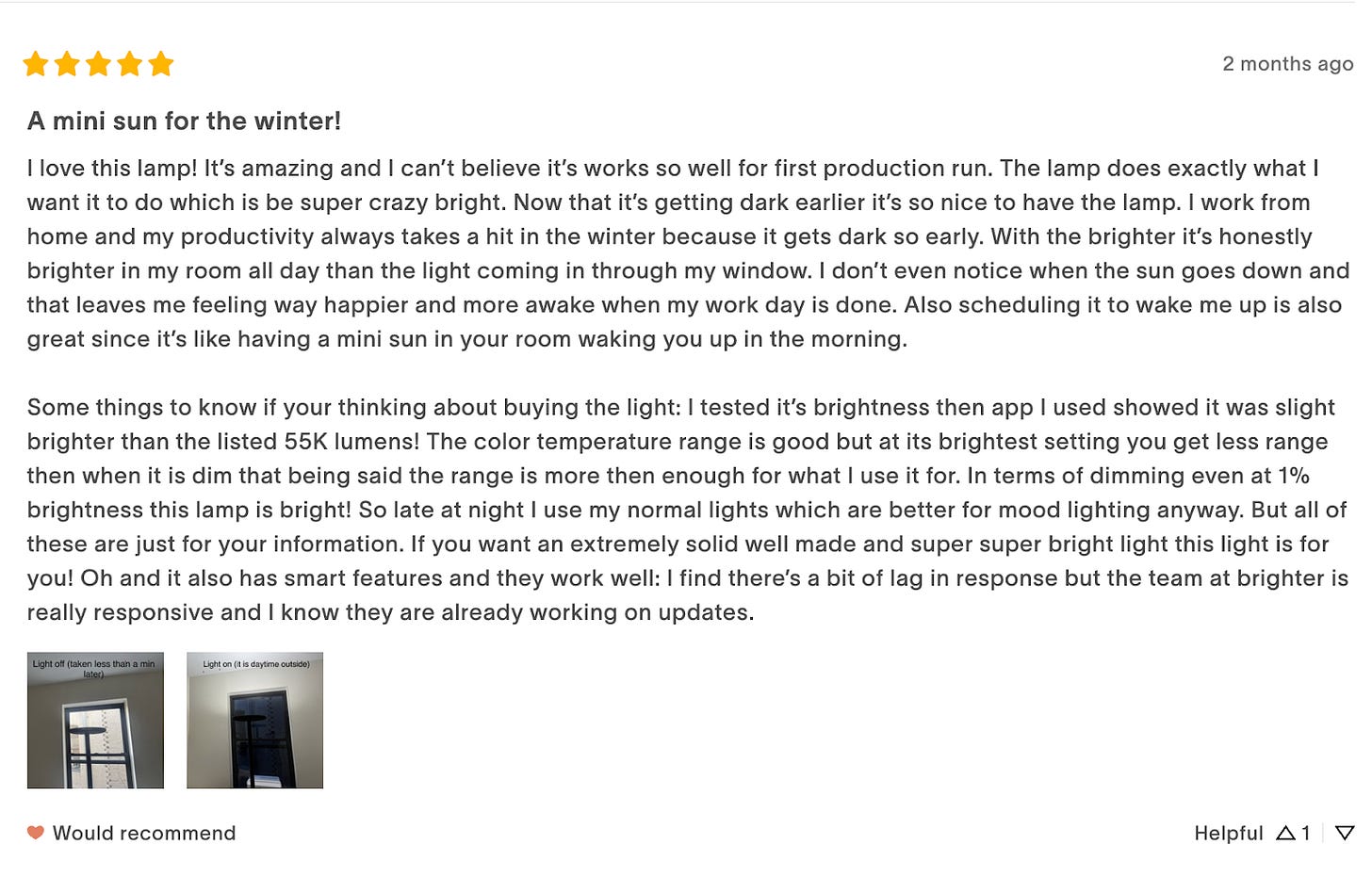
Early customers give some good reviews:
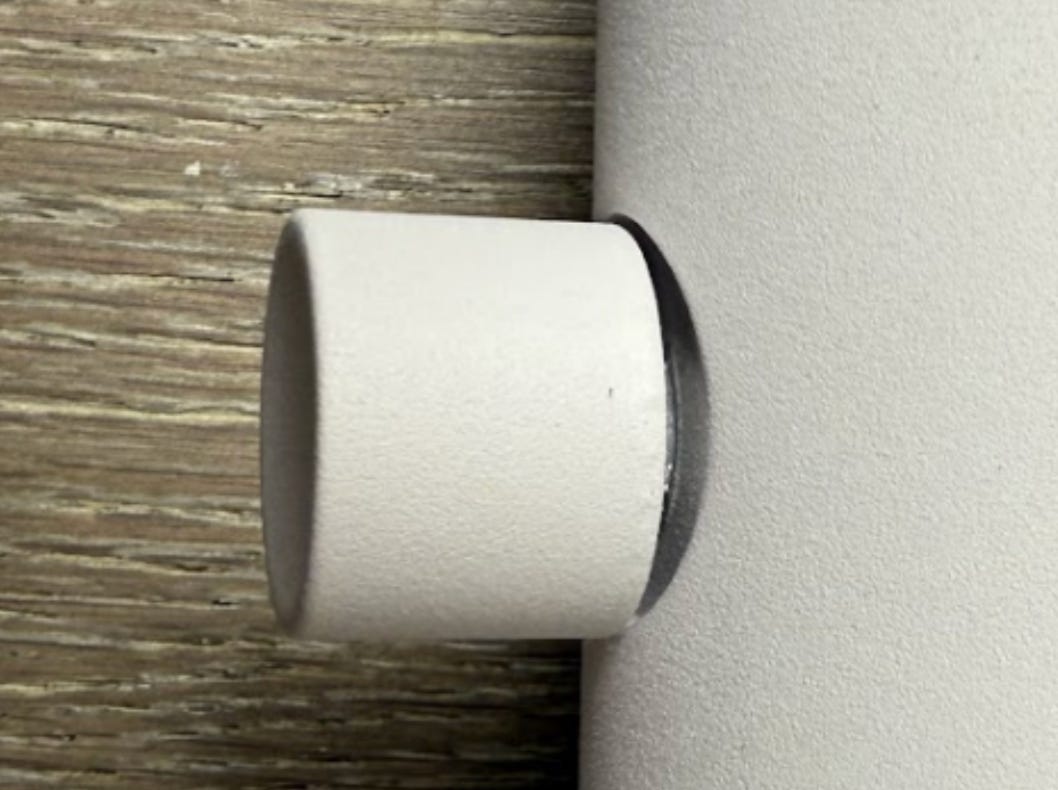
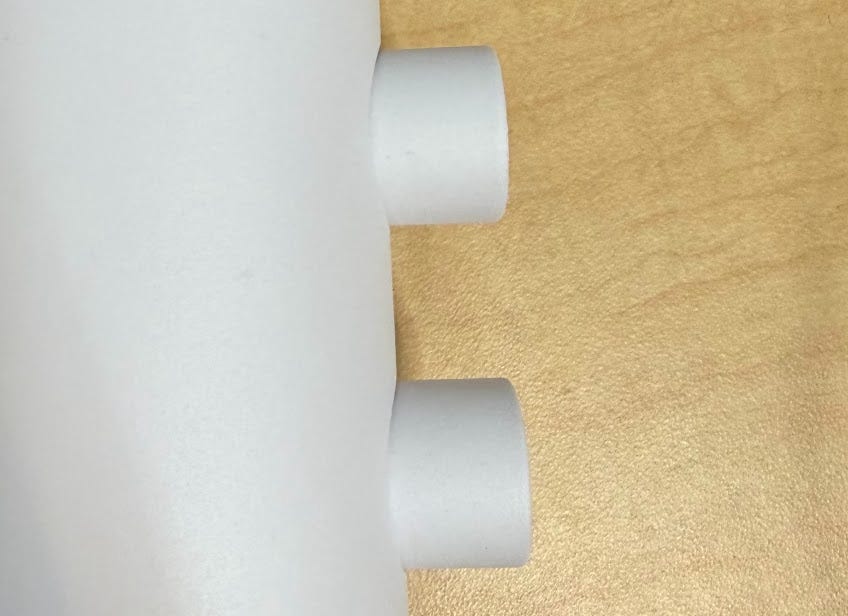
People like the light! A big SF startup orders a lot more. However, there is one issue I hear multiple times: the knobs are scraping and feel horrible. With days until the 500 units are loaded into the container, I frantically call with the engineering team and factory. Obviously this shouldn’t be happening, we designed a gap between the knobs and the wall to spin freely. After rounds of back and forth and measurements, we figure out in the design for manufacturing (DFM) process, the drawings the CNC sub-supplier received did not have the label for spacing between the knobs, resulting in a 0.5mm larger distance than intended. Especially combined with the white powder coating which was thicker than the black finish, this caused some knobs to scrape.
Miraculously, within the remaining days before shipment, the factory remakes & powder coats 1000 new knobs that are 1mm smaller in diameter.
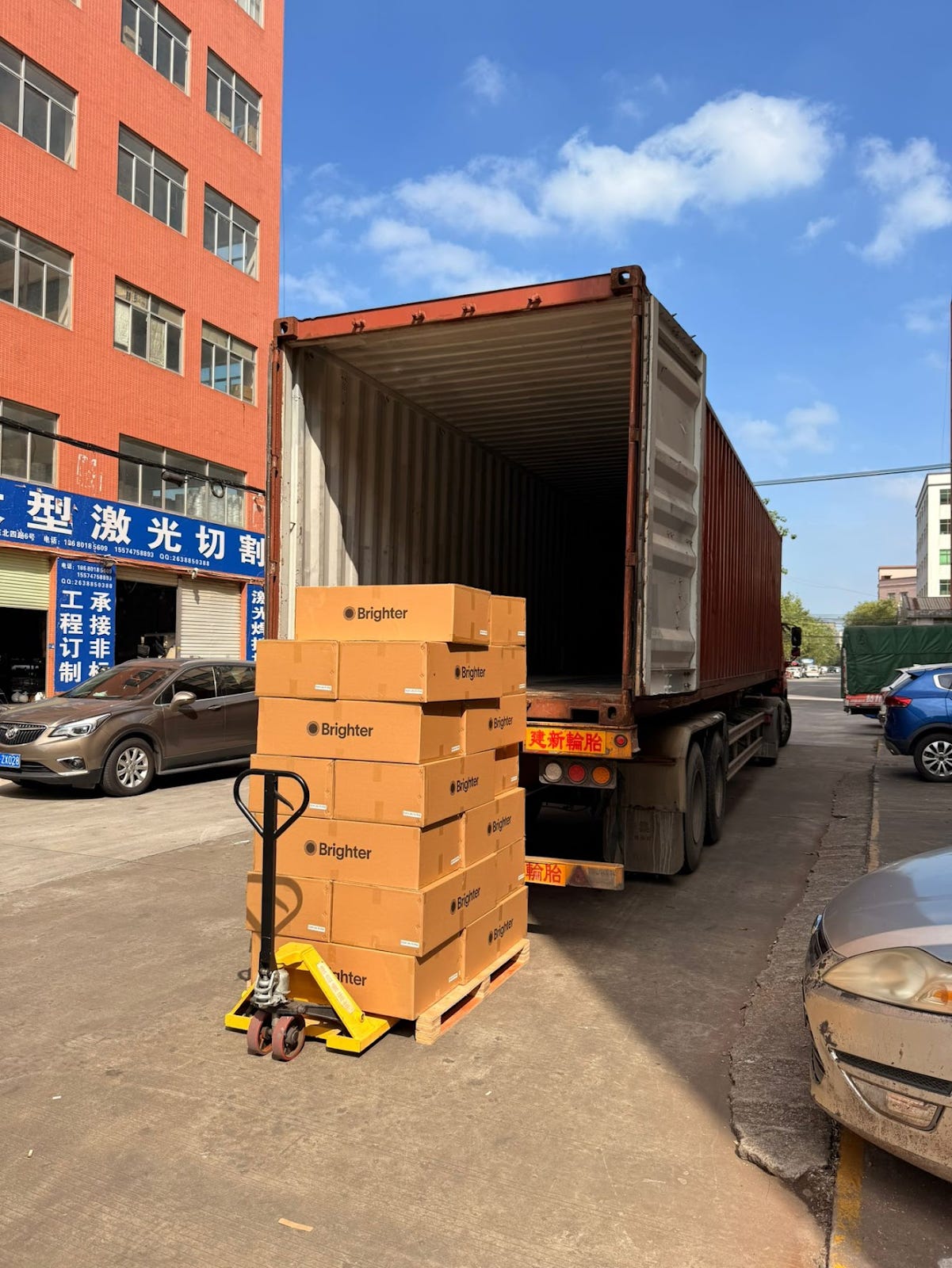
The factory sends me photos of the container being loaded. I have 3 weeks until the lamps arrive in the US — I enjoy the time without last minute engineering problems, albeit knowing inevitably problems will appear again when customers start getting their lamps.
The lamps are processed by our warehouse Monday, Dec 12th, and shipped out directly to customers via UPS. Starting Wednesday, around ~100 lamps are getting delivered every day. I wake up to 25 customer support emails and by the time I’m done answering them, I get 25 more. The primary issue people have is the bottom wires are too short compared to the tubes.
It was at this point I truly began to appreciate Murphy’s law. In my case, anything not precisely specified and tested would without fail go wrong and bite me in the ass. Although we had specified the total length of the cable, we didn’t define the length of cable protruding from the base. As such, some assembly workers in the factory put far too much wire in the base of the lamp, not leaving enough for it to be assembled. Luckily customers were able to fix this by unscrewing the base, but far from an ideal experience.
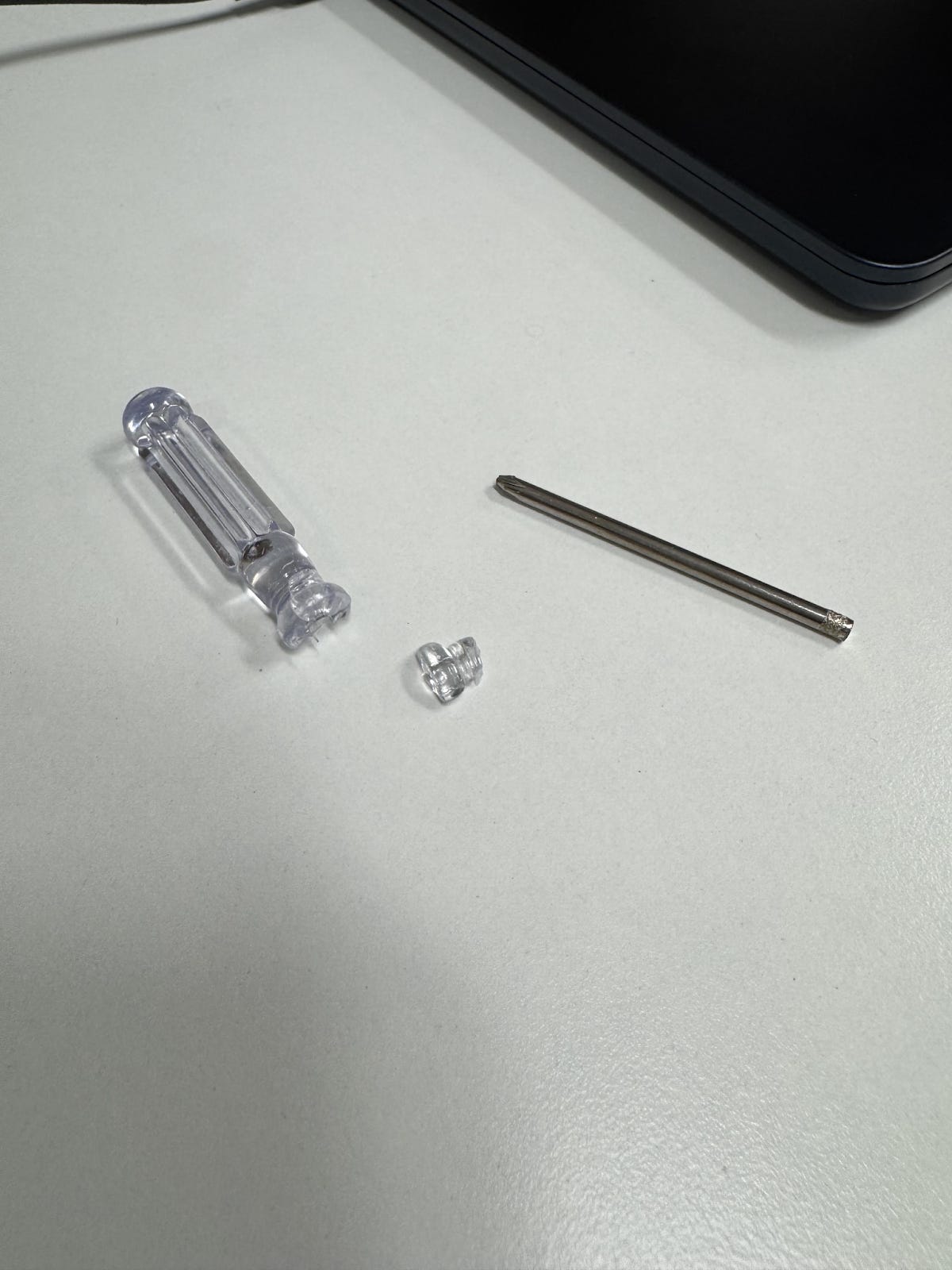
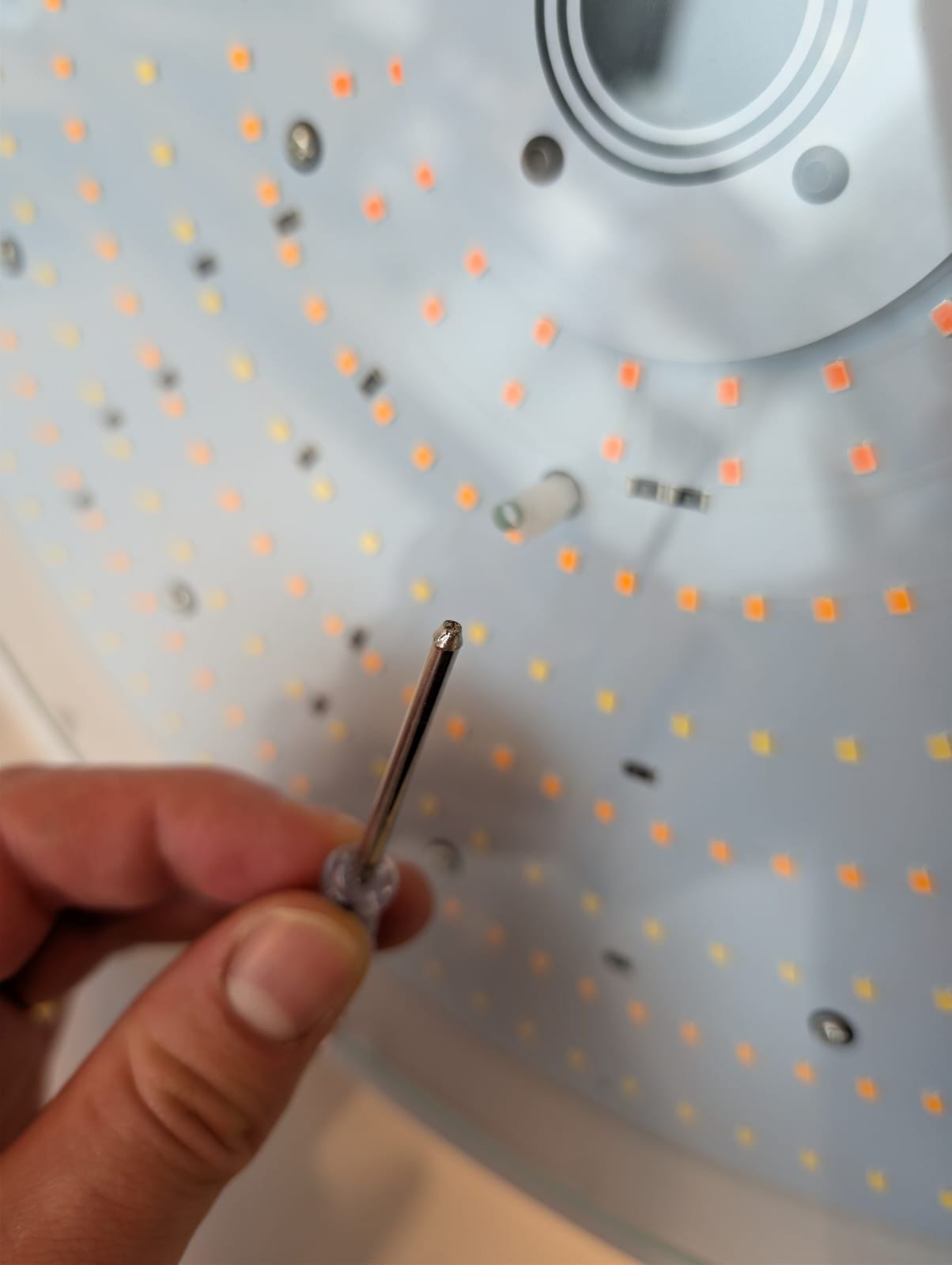
There were other instances of quality control where I laughed at the absurdity: the lamp comes with a sheet of glass that goes over the LEDs, and a screwdriver & screws to attach it. For one customer, the screwdriver completely broke. (First time in my life I’ve seen a broken screwdriver…) For others, it came dull. The screwdriver sub supplier also shipped us two different types of screws, some of which were perfect, and others which were countersunk and consequently too short to be actually screwed in.
Lessons Learned
1. Plan way, way more.
Coming from software, the most planning you’re exposed to is linear tickets, sprints, and setting OKRs. If you missed a deadline, it’s often because you re-prioritized, so no harm done.
In hardware, the development lifecycle of a product is many months. If you mess up tooling, or mass produce a part incorrectly, or just sub-optimally plan, you set back the timeline appreciably and there’s nothing you can do but curse yourself. I found myself reaching for more “old school” planning tools like Gantt charts, and also building my own tools. Make sure you have every step of the process accounted for. Assume you’ll go through many iterations of the same part; double your timelines.
In software, budgeting is fairly lax, especially in the VC funded startup space where all you need to know is your runway (mainly calculated from your employee salaries and cloud costs).
With [profitable] hardware businesses, your margin for error is much lower. Literally, your gross margin is lower! If you sell out because you miss a shipment or don’t forecast demand correctly, you lose revenue. If you mis-time your inventory buying, your bank account can easily go negative. Accounting is a must, and the more detailed the better. Spreadsheets are your best friend. The funding model is also much different: instead of relying heavily on equity, most growth is debt-financed. You have real liabilities!
2. Overcommunicate. Overspecify. Follow Up.
Anything that can go wrong will go wrong. Anything you don’t specify will fail to meet the implicit specification. Any project or component not actively pushed will stall. At previous (software) companies I’ve worked at, if someone followed up on a task, I took it to mean the task was off track and somebody was to blame. With a hardware product, there are a million balls in the air and you need to keep track of all of them. Though somewhat annoying, constant checkins simply math-out to be necessary. The cost of failure or delays is too high. Nowadays as a container gets closer to shipment date, I have daily calls with my factories. I found myself agreeing with a lot of Ben Kuhn’s blog post on running major projects (his blog post on lighting was also a major inspiration for the product).
3. Test everything, often, on many units
When I worked at Meta, every PR had to be accompanied with a test plan. I took that philosophy to Brighter, trying to rigorously test the outcomes we were aiming for (thermals, lumens, power, etc…), but I still encountered surprising failures. In software if you have coverage for a code path, you can feel pretty confident about it. Unfortunately hardware is almost the opposite of repeatable. Blink and you’ll get a different measurement. I’m not an expert, but at this point I’ve accepted the only way to get a semblance of confidence for my metrics is testing on multiple units in different environments.
4. Geopolitics matter
As someone who generally stays out of politics, I didn’t know much about the incoming administration’s stance towards tariffs, though I don’t think anyone could have predicted such drastic hikes. Regardless, it’s something you should be acutely aware of; take it into consideration when deciding what country to manufacture in, make sure it’s in your financial models with room to spare, etc…
5. Visit your suppliers early
I wish I had visited my suppliers much earlier, back when we were still prototyping with them. Price shouldn’t be an issue — a trip to China is going to be trivially cheap compared to buying inventory, even more so compared to messing up a manufacturing run due to miscommunication. Most suppliers don’t get international visitors often, especially Americans. Appearing in person conveys seriousness, and I found it greatly improved communication basically immediately after my first visit. Plus China is very different from the US and it’s cool to see!
What Did I Do Right?
To me, this process has felt like an exercise in making mistakes and learning painful lessons. However, I think I did do a couple of key things right:
1. Validated the market
The first thing I did before starting manufacturing—and even before the crowdfunding campaign—was setting up a simple website where people could pay $10 to get a steep discount off the MSRP. Before I committed time and money, I needed to know this would be self-sustaining from the get go. It turns out that people were happy to give their email and put down a deposit, even when the only product photos I had were from a render artist on fiverr!
2. Charged a sustainable amount
From talking to other hardware founders, these kinds of mistakes happen to everyone; hardware is hard as they say. It’s important to have a healthy enough business model to stomach these mistakes and still be able to grow.
Coolest Cooler had an incredibly successful crowdfunding campaign, partly because they packed a lot of features into a very attractively priced product. Unfortunately, it was too attractively priced, and partway through manufacturing they realized they didn’t have enough money to actually deliver all the units, leading to a slow and painful bankruptcy.
3. Prioritized customer support
When the first 500 units were being delivered, I knew there were bound to be issues. For that first week, I was literally chronically on my gmail. I would try to respond to every customer support issue within 1-2 minutes if possible (it was not conducive to my sleep that many of our customers were in the EU).
Some customers still had some issues with the control tube knobs & firmware. I acknowledged that they were subpar and decided to re-make the full batch of control tubes properly (with the correct knob spacing), as well as updated firmware & other improvements, and ship them to customers free of charge.
Overall, it’s been a very different but incredibly rewarding experience compared to working as a software engineer. It’s so cool to see something I built in my friends houses, and equally cool when people leave completely unprompted reviews:














My man cooking so hard
Thanks for sharing your insights! Not that many write about making and selling a hardware product.